FAQs About Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer begins when the cells lining the inside of the bladder grow abnormally and uncontrollably, forming tumors. Understanding this disease better allows doctors, patients, and caregivers to make informed choices about its management. Here are some questions and answers about cancer of the bladder:
Table of Contents
What Are Some Common Symptoms of Bladder Cancer?
Blood in the urine, or hematuria, is an early symptom of bladder cancer and can cause the urine to appear pink, orange, or red. Other early signs include increased urgency and frequency of urination and pain during urination. As the cancer progresses, it can cause pelvic pain, lower back pain, loss of appetite, and unintended weight loss, though these may also result from other conditions. Doctors can use cystoscopy, biopsies, imaging scans, and urine tests to make a diagnosis.
What Are the Associated Risk Factors?
Prolonged occupational exposure to diesel fumes, rubber manufacturing chemicals, and other carcinogens may raise cancer risks. Smoking introduces harmful substances that can damage the bladder lining, raising the risk for smokers. Age and gender are also contributing factors, as men older than 55 have an increased risk. A family history of bladder cancer may indicate a genetic component. Reducing carcinogen exposure by wearing protective equipment at work and stopping smoking can help reduce the risk.
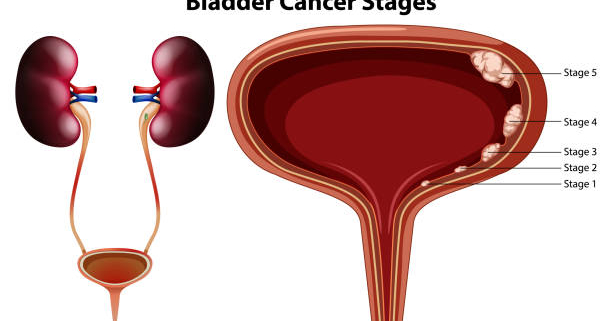
What Are the Stages of This Type of Cancer?
Doctors stage cancer based on how far it has spread. Early-stage tumors remain confined to the bladder lining surface. Mid-stage cancers penetrate partway or completely through the bladder wall. Late-stage bladder cancer breaches the bladder wall, invading nearby organs like the prostate in men and the uterus in women. The latest stage indicates the spread to distant organs like the liver and lungs.
What Are the Treatment Options?
For early-stage bladder cancer, urologists offer procedures such as cystoscopic tumor removal to prevent disease progression. Robotic-assisted laparoscopic surgery provides a minimally invasive option for partial or radical cystectomy to excise tumors. Possible follow-up chemotherapy and radiation therapy address any remaining or metastatic cancer cells. Participating in cancer clinical trials may also provide access to new therapies.
Are There Lifestyle Choices That Affect Recurrence?
Certain lifestyle choices may help patients maintain long-term cancer remission after treatment. Regular exercise and a nutrient-rich diet help patients maintain a healthy weight, as excess body weight may be linked to a higher chance of returning bladder cancer. Avoiding tobacco reduces carcinogen exposure. To promote overall health and wellness in cancer survivors, patients can avoid or limit alcohol consumption and focus on including a variety of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains in their diet.
Seek Cancer Treatment Today
Understanding cancer of the bladder can help patients and caregivers identify symptoms early, seek diagnosis, and access life-extending treatment for better outcomes. If experiencing concerning symptoms like hematuria and the inability to empty the bladder fully, patients can contact a urologist for support and diagnosis. Urologists may provide patients with access to advanced laparoscopic procedures, chemotherapy, radiation, and clinical research trial options. Call an experienced urologist today to discuss your symptoms and create a personalized care plan.
You May Also Like

Seattle Mariners vs Yankees Match Player Stats
November 17, 2024
Remembering Sean Flaherty Obituary Stow Ohio
October 27, 2024

